How to operate a drone safely and effectively is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the regulations, appreciating the technology, and unlocking the creative potential of aerial photography. This guide delves into every aspect, from pre-flight checks and airspace regulations to advanced flight maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues. We’ll equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly and capture breathtaking aerial footage.
We’ll cover everything from the basics of understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes to more advanced techniques like planning complex flight paths and utilizing waypoint systems. We’ll also explore the nuances of drone camera operation, ensuring you capture high-quality photos and videos. Safety is paramount, so we’ll detail essential pre-flight checks and discuss relevant regulations to ensure your flights are both successful and legal.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to relevant regulations and safety protocols. This section Artikels essential guidelines to ensure safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Licensing and Certification, How to operate a drone
Drone regulations vary by country and region. In many places, drone operators must obtain licenses or certifications depending on the drone’s weight, intended use, and the airspace involved. For example, in the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires registration for most drones and may require a Remote Pilot Certificate for commercial operations. Check your local aviation authority for specific requirements in your area.
Airspace Restrictions and Regulations
Drone flights are restricted in certain airspace, including airports, military bases, and areas with controlled airspace. It’s crucial to check airspace maps and avoid flying near these restricted zones. Many apps and websites provide up-to-date airspace information. Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone and be aware of surrounding obstacles and other aircraft.
Pre-Flight Checks
A thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe operation. This involves a step-by-step process to ensure your drone is ready for flight.
- Check battery levels: Ensure the drone battery is fully charged and connected securely.
- Verify GPS signal: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff.
- Inspect propellers: Check for damage or wear on the propellers. Replace any damaged propellers before flight.
- Examine the drone body: Look for any visible damage or loose parts.
- Test the controller: Ensure the remote controller is functioning correctly and properly connected to the drone.
- Review weather conditions: Do not fly in inclement weather, such as strong winds or rain.
Drone Safety Feature Comparison
Different drone models offer varying safety features. The table below provides a comparison of some common features.
| Drone Model | GPS Fail-Safe | Return-to-Home (RTH) | Obstacle Avoidance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Yes | Yes | No |
| Model B | Yes | Yes | Yes (front and bottom) |
| Model C | Yes | Yes | Yes (360°) |
| Model D | No | Yes | No |
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Mastering drone controls and understanding different flight modes are essential for safe and efficient operation. This section details the functionality of a standard drone remote and various flight modes.
Drone Remote Control Functions
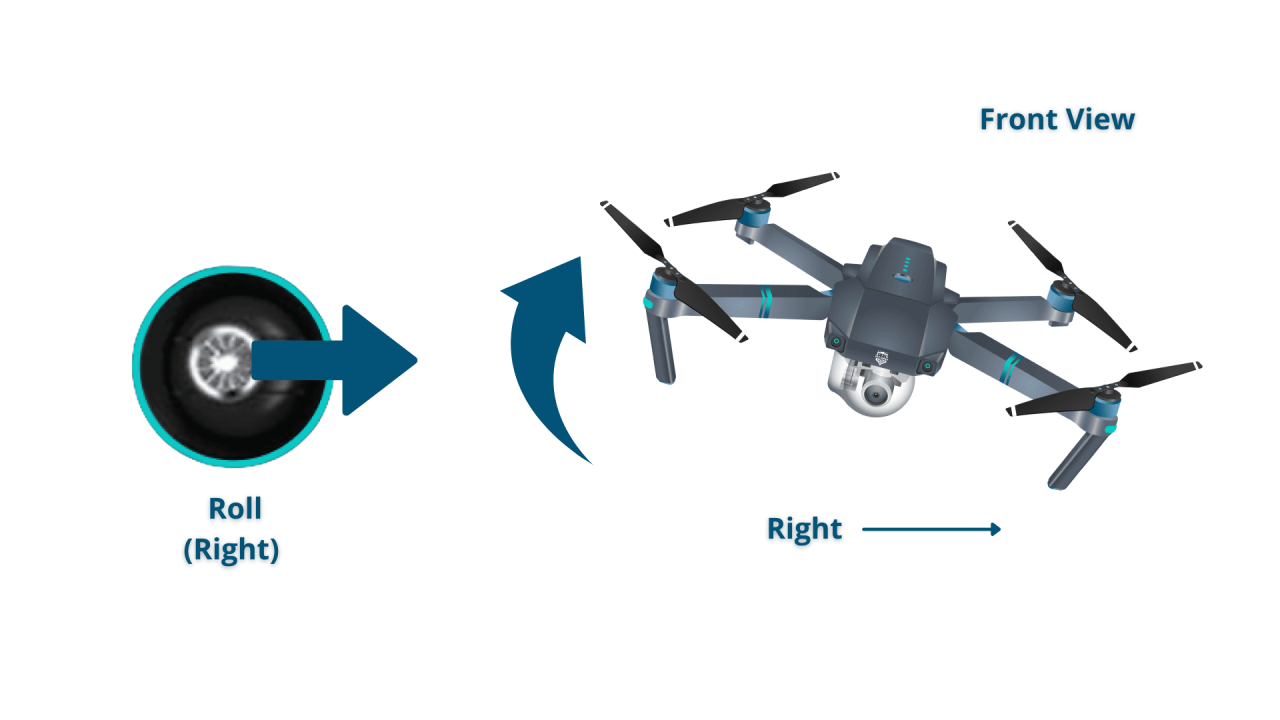
Standard drone remotes typically have two control sticks and several buttons. The left stick controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls roll (side-to-side movement) and pitch (forward and backward movement). Buttons often control functions such as takeoff, landing, return-to-home, and camera controls.
Flight Modes
Drones often offer various flight modes to suit different skill levels and flight scenarios.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Enables higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for positioning and stability, helpful for precise flight and return-to-home functionality.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of its position in space.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are crucial for stable and reliable flight. Calibration procedures vary by drone model, but generally involve performing a series of movements as instructed by the drone’s software.
Drone Takeoff, Maneuvering, and Landing Flowchart
A structured approach to takeoff, maneuvering, and landing is essential for safety. The following flowchart illustrates the steps:
Start –> Pre-flight Checks –> Power On Drone & Controller –> GPS Acquisition –> Calibration (if needed) –> Takeoff –> Maneuvering (using control sticks) –> Landing Sequence Initiation –> Safe Landing –> Power Off –> Post-Flight Inspection –> End
Drone Camera Operation and Photography Techniques
Drones equipped with cameras offer incredible opportunities for aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is key to capturing high-quality content.
Drone Camera Settings
Drone cameras typically offer adjustable settings such as ISO (sensitivity to light), shutter speed (exposure time), and aperture (controls the amount of light entering the lens). Adjusting these settings allows for control over image brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial footage involves a systematic approach.
- Choose the right lighting: Avoid harsh midday sun; softer light (golden hour) generally produces better results.
- Plan your shot: Consider composition, angles, and subject matter beforehand.
- Use a steady hand (or gimbal): Minimize camera shake for smooth footage.
- Experiment with settings: Adjust ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to achieve desired effects.
- Review and edit: Post-processing can enhance the quality of your aerial photos and videos.
Optimal Lighting Conditions and Shooting Angles
The best lighting conditions for aerial photography are typically during the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) or on overcast days. Shooting angles can significantly impact the composition and mood of your shots. Experiment with various angles to find what works best for your subject.
Best Practices for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Creating visually engaging aerial shots requires careful planning and execution.
- Use leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Employ the rule of thirds for balanced composition.
- Incorporate symmetry and patterns for visually appealing shots.
- Vary your angles and perspectives to add dynamism.
- Pay attention to the background and foreground elements.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drones can experience malfunctions. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common issues.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Several problems can occur during drone operation. Addressing them promptly is crucial.
- Low Battery: Check battery level and charge if necessary. Consider carrying spare batteries.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear skies and move to an area with a strong GPS signal. Recalibrate the GPS if needed.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage. If a motor is malfunctioning, it may need replacement.
- Controller Issues: Check battery level and connections. Try restarting the controller and drone.
- Propeller Damage: Inspect propellers for damage and replace as needed.
Tips for Preventing Common Drone Problems
- Regularly inspect the drone for damage.
- Keep the drone clean and dry.
- Store the drone in a safe and protected environment.
- Use high-quality batteries.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions for operation and maintenance.
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone. This section details necessary maintenance tasks and storage procedures.
Drone Maintenance Tasks
Maintaining your drone involves several key steps.
- Inspect propellers for damage and replace as needed.
- Clean the drone body with a soft cloth and gentle cleaner.
- Check the gimbal for proper functionality.
- Inspect the camera lens and clean if necessary.
- Check all connections and screws for tightness.
Cleaning and Storage Methods
Proper cleaning and storage protect your drone from damage and extend its lifespan.
- Clean the drone with a soft, dry cloth.
- Store the drone in a dry, cool, and dust-free environment.
- Store batteries separately in a designated storage case.
- Protect the drone from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight.
Routine Drone Maintenance Checklist

Use this checklist for regular maintenance.
- [ ] Inspect propellers for damage
- [ ] Clean the drone body
- [ ] Check gimbal functionality
- [ ] Inspect camera lens
- [ ] Check all connections and screws
- [ ] Inspect and charge batteries
Replacing Drone Components
Replacing components like propellers and batteries is straightforward. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions. Generally, it involves removing the damaged component and attaching the new one securely.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered basic drone operation, you can explore advanced maneuvers and flight planning techniques. This section covers advanced flight techniques and flight planning software.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips and rolls, require practice and skill. These maneuvers should only be attempted in open, safe areas away from obstacles and people. Always prioritize safety.
Planning and Executing Complex Flight Paths
Planning complex flight paths often involves using waypoint systems or flight planning software. These tools allow you to pre-program a series of points for the drone to follow, enabling intricate aerial shots and surveys.
Waypoint Systems and Flight Planning Software

Many drone manufacturers offer their own flight planning software, while third-party options provide additional features and capabilities. These programs allow you to create detailed flight plans, including waypoints, altitude, speed, and camera settings.
A Challenging Aerial Maneuver: The Helix
Imagine a drone ascending in a spiral pattern, maintaining a constant radius and gradually increasing altitude. The drone’s camera is pointed downwards, capturing a circular path as it rises, creating a dynamic and visually engaging shot. This maneuver requires precise control and a good understanding of the drone’s capabilities.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that blends technology, skill, and creativity. By understanding the regulations, mastering the controls, and implementing proper maintenance, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible operation is key to ensuring safe and enjoyable flights, and we encourage continued learning and exploration to further enhance your aerial capabilities. The skies await!
FAQ Guide: How To Operate A Drone
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS assistance and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models known for their ease of use and stability.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight mode). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, it will typically enter a failsafe mode. Most drones will attempt to return to the last known GPS location. If this fails, carefully guide it down using visual flight mode.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
